Barometers of Vitality: The Key Indicators That Signal Good Health and Overall Well-Being
Discover the crucial indicators of good health and well-being in 'Barometers of Vitality.' Explore the key signs that signal a thriving, balanced life. Elevate your wellness journey today!
1) Introduction to
Vitality
Vitality is defined as a
condition of good health, vitality, and general well-being. It includes
physical, mental, and emotional health and is defined by vigor or vitality,
allowing people to live active and meaningful lives.
b) The Importance of Good Health and Well-Being
Good health and well-being are
essential for having a fulfilling life. They have an impact on our capacity to
achieve our objectives, participate in meaningful activities, and enjoy life to
the fullest. Maintaining excellent health entails not just avoiding disease but
also actively cultivating our physical and emotional moods.
c) Purpose of the Blog
The goal of this blog is to give
useful knowledge and insights about how to develop and sustain vitality in all
parts of life, such as physical health, diet, and mindfulness. We hope to
provide readers with knowledge and practical ideas to help them make better
informed decisions for a healthier, more meaningful life.
d) Preview of Key
Indicators of Vitality
In this article, we will look at
key markers that are important in analyzing and enhancing vitality. These
indicators include physical health measurements such as BMI and blood pressure,
as well as nutrition and mindful eating. Readers may take proactive efforts to
improve their vitality by recognizing and regulating these markers.
2) Importance of Physical
health in maintaining Vitality
a) Body Mass Index (BMI)
(Maintaining Vitality)
Body Mass Index, or BMI, is a widely used metric that offers a quick and easy numerical estimate of a person's "fatness" or "thinness," allowing health practitioners to address weight concerns with their patients in a more objective manner. It is computed by dividing a person's weight in kilograms by their height in meters squared. BMI is a valuable tool since it corresponds to the amount of body fat in the majority of persons. It is used as a screening tool in adults to identify possible weight concerns. It is not, however, a diagnostic instrument. A healthcare practitioner would need to do additional evaluations to establish if extra weight is a health risk. Skinfold thickness measures, dietary and physical activity evaluations, family history, and other acceptable health tests may be included in these examinations.
While BMI is a valuable tool for identifying populations at risk owing to high body fat, it is not without limitations. It has various drawbacks, most notably the fact that it does not directly assess body fat. As a result, certain people, such as athletes, may have a BMI that indicates they are overweight while having no additional body fat. Others, especially the elderly, may have a low BMI yet still have considerable body fat. In certain circumstances, waist circumference, skinfold thickness, or other more direct techniques of assessing body fat may be more informative.
Furthermore, BMI does not discriminate between weight related to muscle and weight related to fat. As a result, two persons with the same BMI but differing body fat percentages might exist. An athlete, for example, may have a high BMI due to greater muscularity rather than increased body fat.
A healthy BMI normally lies
between 18.5 and 24.9. A BMI less than 18.5 denotes underweight, whereas a BMI
more than 24.9 indicates overweight or obesity. Maintaining a healthy BMI is
critical for lowering the risk of a variety of health concerns, such as heart
disease, diabetes, and joint difficulties.
b) Blood Pressure )
(Maintaining Vitality)
i) Significance of Blood Pressure
Blood pressure is a key health indicator that measures the force exerted by blood on the artery walls as it is pumped throughout the body by the heart. It is the amount of force used by your blood to go through your arteries. When your heart beats, it exerts effort to drive oxygen-rich blood into your arteries, which subsequently transport it to your body's cells and tissues. Blood pressure is not constant and might fluctuate depending on what you're doing. For example, when you exercise or become enthusiastic, your blood pressure rises. Your blood pressure is lower when you are resting.
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a serious health risk. It is known as the "silent killer" since it normally causes no symptoms. It can harm your heart, kidneys, and brain before you realize there is a problem. Hypertension can cause major health issues such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and even damage to your eyes' blood vessels.
Blood pressure monitoring is critical for early detection and treatment of hypertension. Regular blood pressure readings are advised, particularly for adults, as the risk of hypertension increases with age. Home blood pressure monitoring is one of the most effective strategies to help control hypertension because it records your blood pressure more precisely over time and provides your doctor with a better picture of your average daily reading.
ii) Normal Blood Pressure Values
Normal blood pressure levels are usually about 120/80 mm Hg, which is measured in two parts: systolic and diastolic pressure. The first, systolic pressure, is the maximum arterial pressure during systole (when the heart beats). The second, diastolic pressure, is the lowest arterial pressure measured during diastole (when the heart is at rest).
Consistently high levels might indicate hypertension. A hypertensive emergency or crisis is defined as blood pressure more than 180/120 mm Hg. A measurement less than 90/60 millimeters of mercury, on the other hand, is considered a low blood pressure reading, which may be normal for some people but may suggest a concern for others. Maintaining a healthy blood pressure level is critical for general health and may be accomplished by lifestyle modifications such as a well-balanced diet and frequent exercise. These practices can aid in the prevention and treatment of high blood pressure. It's crucial to remember that blood pressure can be impacted by a variety of factors, including the time of day, activity, the foods you eat, stress, and others. As a result, having frequent check-ups and monitoring your blood pressure at home is suggested for a more accurate knowledge of your average daily reading.
c) Restful Sleep Patterns
(Maintaining Vitality)
i) Link Between Sleep and Health
Sleep is essential for physical health because it allows the body and brain to recoup and regenerate. Sleep insufficiency or lack of sleep can cause a variety of health issues. Obesity, heart disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, and stroke are examples.
Sleep deprivation can disrupt the body's hormonal balance, resulting in increased appetite and overeating. This is due to increased ghrelin synthesis, a hormone that promotes hunger, and decreased leptin levels, a hormone that indicates fullness.
Sleep is also important for heart health. Blood pressure usually drops during sleeping, and a lack of sleep can result in a higher daily average blood pressure, raising the risk of heart disease and stroke. Sleep deprivation can also have an impact on insulin control, resulting in higher glucose levels and an increased risk of developing Type 2 diabetes.
Adequate sleep also improves the immune system. The amount of particular T-cells, cytokines, and other critical immune system components increases during sleep. Inadequate sleep can impair the immune system's response to viruses and other illnesses.
Sleep and mental and emotional wellness are inextricably linked. It has been linked to depression, anxiety, bipolar illness, and other disorders. Poor sleep, especially insomnia, can contribute to the onset and progression of mental health disorders.
Sleep deprivation has been shown to decrease attention, working memory, and long-term memory. It can also have an impact on decision-making and the capacity to assimilate new information when doing difficult jobs.
Sleep is required for memory processing. Your brain begins organizing and consolidating memories during the third non-rapid eye movement stage of your sleep cycle. Sleep deprivation might impair your capacity to retain key facts.
People who don't get enough sleep may struggle to regulate their emotions, make smart decisions, and cope with various facets of everyday living. Sleep deprivation can also contribute to mental health problems like depression and raise one's risk of suicide.
Every day, including on weekends,
go to bed and wake up at the same hour. Consistency aids in the regulation of
your body's internal clock, making it simpler to sleep and wake up naturally.
Choose a mattress and pillows that are comfortable and give adequate support
for your body. A mattress that is overly old or unpleasant might cause sleep
disruption. At least an hour before going to bed, avoid using electronic
devices such as cellphones, tablets, and laptops. Screen blue light can
interfere with your body's generation of melatonin, a hormone that governs
sleep. To rest your thoughts before going to bed, try deep breathing,
meditation, or progressive muscle relaxation. Get some natural sunshine during
the day, particularly in the morning. Natural light aids in the regulation of
your body's internal clock and the maintenance of your sleep-wake cycle.
3) Role of Nutrition in maintaining
Vitality
a) Balanced Diet (Maintaining
Vitality)
i) Components of a Balanced Diet
Fruits, vegetables, whole grains,
lean meats, and healthy fats are all part of a well-balanced diet. These
components supply critical elements such as vitamins, minerals, fiber, and
antioxidants, all of which are required for good health.
ii) Importance of Nutrient-Rich Foods
Nutrient-dense diets are essential for sustaining physical health. A healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy can help lower the risk of heart disease by keeping blood pressure and cholesterol levels stable. Consuming omega-3 fatty acid-rich oily fish may also reduce the risk of heart disease.
A calcium-rich diet, such as dairy products and some vegetables, can help to keep teeth and bones healthy and reduce bone loss linked with age. Furthermore, a balanced diet can aid in weight maintenance, lowering the risk of weight gain and associated health conditions such as type 2 diabetes.
Foods high in nutrients can also help stop the cycle of malnutrition and obesity. Foods with high nutrient density have a low calorie to nutrient ratio, allowing for the intake of nutritionally adequate meals without raising the risk of obesity.
b) Hydration (Maintaining
Vitality)
i) Role of Hydration in Health
Proper hydration is necessary for the proper functioning of several biological systems, including digestion, circulation, and temperature management. Dehydration can cause a range of health issues, including headaches and weariness.
Water is essential for digestion since it aids in the breakdown of food, allowing nutrients to be absorbed. It also helps the gastrointestinal tract run smoothly, avoiding constipation and other digestive disorders. Water is an important component of saliva, which helps to moisten food and aids in chewing and swallowing. Furthermore, water is required for the creation of gastric juices as well as the mucus that lining the stomach and protects it from acidic digestive acids.
Hydration is needed for adequate blood volume, which is required for healthy circulation and the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to cells. When the body is dehydrated, blood flow is diminished, which raises body temperature and puts pressure on the heart. Staying hydrated promotes good circulation by improving blood flow throughout the body.
Water is essential for maintaining body temperature, particularly during activity or in hot conditions. It aids in heat dissipation through sweating, reducing overheating and guaranteeing peak performance. When the body is exposed to a hot environment, water helps to drain heat away from the center of the body and maintain a steady body temperature. Water, on the other hand, helps to retain heat and keep the body warm when it is exposed to a chilly environment.
Mild dehydration can cause blood pressure, heart rate, and body temperature issues. Severe dehydration can result in more serious problems like weakness, disorientation, seizures, brain damage, and even death. Staying hydrated can aid in the prevention of these issues and the maintenance of general health.
ii)
Daily Water Intake Recommendations
Water is required for a variety
of body processes such as waste removal, temperature regulation, joint
lubrication, and tissue protection. The daily fluid consumption recommendation
for males is around 15.5 cups (3.7 liters) and 11.5 cups (2.7 liters) for
women, which includes fluids from drinks and meals. Although eight glasses of
water per day is a good aim, actual needs might vary depending on factors such
as activity, environment, overall health, and life phases (e.g., pregnancy).
c) Mindful Eating (Maintaining
Vitality)
Focusing on the sensory experience of eating, such as taste, smell, and texture, is what mindful eating implies. It promotes a positive relationship with food, reduces overeating, and increases meal pleasure. Here are some of the advantages of mindful eating.
Mindful eating can result in a better connection with food and general well-being. Individuals can become more aware of their body's hunger and fullness cues by paying attention to the sensory experience of eating, leading to wiser food choices and portion management. This can lead to better weight control, improved digestion, and enhanced meal pleasure.
By encouraging people to slow down and taste their meal, mindful eating can help minimize overeating and binge eating. This enables people to detect fullness and have more control over their eating habits. Mindful eating strategies have been proven in studies to be effective in decreasing binge eating and emotional eating.
Mindful eating can improve food satisfaction by concentrating on the sensory experience of eating. This can result in a more rewarding and joyful eating experience, which can lead to a healthier relationship with food and general well-being.
ii) Tips for Practicing Mindful Eating
Readers will find useful
strategies for adding mindfulness into their eating habits, such as slowing
down when eating, enjoying each mouthful, and paying attention to hunger and
fullness indicators.
4) Role of Mental and
Emotional Well-Being in maintaining Vitality
a) Stress Management (Maintaining
Vitality)
Stress may have a significant
impact on both physical and mental health. Chronic stress may cause a variety
of health concerns, including cardiovascular difficulties including high blood
pressure and heart disease, as well as weakened immunological function.
Furthermore, stress can aggravate mental health disorders such as anxiety and
depression. It can also contribute to unhealthy coping techniques like
overeating or substance misuse, which can have a negative influence on one's
general well-being.
ii) Stress-Reduction Techniques
Individuals can employ a range of stress-reduction tactics to manage and lessen the impact of stress on their health. Relaxation and emotional balancing exercises, physical activities, cognitive tactics, and therapeutic interventions are some of the techniques used.
Activities for relaxation and emotional balancing attempt to soothe the mind and body, fostering a feeling of relaxation and balance. Mindfulness and meditation are examples of these practices.
Mindfulness is a type of meditation that includes focusing on and embracing the present moment without judgment. It assists individuals in being more conscious of their thoughts and emotions, helping them to better handle stress. Mindfulness has been shown to reduce activity in the amygdala, the portion of the brain linked with the stress response, lowering overall stress levels.
Mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) is an 8-week therapy method that consists of weekly group workshops and daily mindfulness activities. It has been shown to be beneficial in the treatment of stress, anxiety, and depression.
Regular exercise, for example, can help reduce stress by releasing endorphins, the body's natural mood boosters.
Exercise can relieve stress by simulating the symptoms of stress, such as the flight or fight reaction. This can assist in reducing the detrimental consequences of stress.
Cognitive methods such as time management and problem-solving talents might help people better handle stress in their lives. By helping individuals to handle their activities and obligations more efficiently, effective time management can help alleviate stress. Problem-solving talents, on the other hand, can assist individuals in more successfully addressing the origins of their stress, so lessening their impact.
b) Emotional Resilience
i) Definition of Emotional Resilience
Emotional resilience is a
person's capacity to adapt and recover from hardship, trauma, or difficult
events. It entails the ability to properly control emotions, have an optimistic
viewpoint, and be mentally adaptable in the face of adversities.
ii) Strategies for Building Resilience
Social support networks are critical for resilience, particularly during difficult circumstances. These networks may include family, friends, or community organizations that offer emotional support, encouragement, and reassurance. They can make people feel less alone during stressful times and can function as a stress buffer.
According to research, having access to social support in all of its forms—emotional support, instrumental assistance, and cognitive support—can help people deal with obstacles more efficiently. Positive social ties are essential for resilience because they reduce stress and improve psychological and physical well-being.
Furthermore, social support networks might be especially important for disadvantaged populations, such as those experiencing financial trouble. Social safety nets can boost resilience in these situations by minimizing adversity and fostering better health outcomes.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is an essential component of resilience development. It is based on the premise that the intensity of our sensations and behaviors is influenced by our ideas. As a result, how we think about unpleasant or challenging events has a significant impact on our basic beliefs and, as a result, our resilience.
CBT promotes people to question and reframe negative ideas, resulting in a more optimistic outlook. This method can help people better manage and control their powerful emotions, allowing them to respond to events more appropriately.
Self-care is critical for increasing emotional resilience. Prioritizing sleep, food, and exercise are examples of habits that can strengthen an individual's physical and mental foundations.
Nurturing and caring to your inner feelings and emotions is one example of emotional self-care. Mindfulness, writing, setting boundaries, and having strong, supportive relationships may all contribute to this.
Limiting your exposure to news, practicing appreciation, utilizing meditation applications, and indulging in soothing hobbies are all examples of self-care activities. These activities can help reduce stress, boost mood, and improve emotional regulation.
To summarize, developing emotional resilience is a dynamic process that combines social support, cognitive-behavioral techniques, and self-care behaviors. Individuals may improve their general well-being by incorporating these tactics into their everyday lives and increasing their capacity to cope with stress and hardship.
c) Positive Relationships (Maintaining
Vitality)
i) Connection Between Relationships and Well-Being
Positive interactions are
important for an individual's mental and emotional well-being. Relationships
that are strong and supportive can bring emotional comfort, alleviate stress,
and improve overall life satisfaction. They also provide a sense of belonging
and purpose, both of which are essential for mental wellness.
ii) Tips for Cultivating Positive Relationships
A healthy relationship is built on effective communication. It entails openly and successfully communicating your views, feelings, and requirements. It's critical to make time to chat without interruptions and to be clear about what you want to say. To communicate your sentiments and desires, use 'I' expressions such as 'I need,' 'I want,' and 'I feel'. Also, make sure your body language matches what you're saying, because nonverbal communication is typically 'heard' and believed.
Active listening is an important component of good communication. It entails paying close attention to the speaker, expressing real interest, and abstaining from interrupting. It's also crucial to solicit feedback from the other person on your listening abilities. Active listening may inspire your spouse to communicate openly and honestly, boosting your connection.
The ability to comprehend and share the sentiments of others is referred to as empathy. It entails placing oneself in the shoes of another person and experiencing their feelings. Empathy may strengthen your relationships by connecting with the ideas and feelings of others. It may also inspire you to take acts that better the lives of others, guide your decision-making, prevent burnout, and aid in dispute resolution.
Trust is an essential component of every relationship. It entails being dependable, consistent, and truthful. Setting and adhering to boundaries is also essential. Boundaries are not only about what you don't want or enjoy in your relationships; they are also about communicating to others around you what you value. Respecting your alone time, for example, might relieve stress in your relationship.
Spending quality time with loved ones and establishing friendships via common hobbies helps strengthen bonds. Building companionship with your spouse by sharing experiences, interests, and worries might help you communicate better.
Conflict resolution skills are essential for maintaining healthy relationships. They make it possible to confront and resolve issues constructively. Empathizing with people might help you avoid being excessively critical or unkind during confrontations. When you have a greater knowledge of another person's point of view, it is simpler to propose a compromise.
To communicate oneself clearly and successfully, get to know yourself and respect your feelings. Regardless matter how much time you spend with someone, keep your personal objectives and progress in mind. Remember that there's a reason people like you in the first place, so don't lose your distinguishing characteristics.
Consider the relationships that function best in your life, what features they have, and how you may incorporate these aspects into other relationships. You can react to other people's feelings in a healthy way if you have a healthy method of expressing your own.
5) Role of Physical Fitness in
maintaining in Vitality
a) Regular Exercise (Maintaining
Vitality)
i) Benefits of Exercise on Health
Regular exercise has several
health advantages. It improves cardiovascular health by increasing circulation,
lowering the risk of heart disease, and controlling blood pressure and
cholesterol levels. Exercise also aids in the maintenance of a healthy weight,
which lowers the risk of obesity-related diseases such as diabetes. Physical
activity also improves mental health by producing endorphins, lowering stress,
and enhancing sleep quality.
ii) Recommended Physical Activity Guidelines
Adults should engage in at least
150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of
vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise each week, as well as muscle-strengthening
exercises on two or more days per week. These suggestions assist people in
maintaining their physical fitness and general health.
b) Flexibility and Mobility (Maintaining
Vitality)
i) Importance of Flexibility and Mobility
Physical fitness requires a high
level of flexibility and movement. They promote joint health, minimize injury
risk, and increase total functional ability. Maintaining flexibility and
mobility becomes increasingly crucial as people age in order to retain
independence and quality of life.
ii) Exercises for Improving Flexibility
Yoga and Pilates are good
stretching activities for increasing flexibility. Incorporating these exercises
into your workout program will help you improve your range of motion and
minimize muscular stiffness. Stretching on a regular basis also increases
relaxation and lowers muscular tension, which contributes to a general sense of
well-being.
c) Strength Training (Maintaining
Vitality)
i) Role of Strength Training in Health
Strength training is essential
for increasing and preserving muscular mass, which normally diminishes with
age. It aids in the improvement of metabolism, bone density, and functional
ability. Furthermore, strength training helps with posture, balance, and injury
avoidance.
ii) Simple Strength-Building Exercises
Bodyweight exercises such as
push-ups, squats, and planks are examples of simple strength-building
exercises. Weightlifting, resistance bands, and machine workouts can all help
you gain strength. To gain the full advantages of strength training,
progressively increase the intensity and complexity of these exercises over
time.
6) Role of Preventive Health
Measures in maintaining Vitality
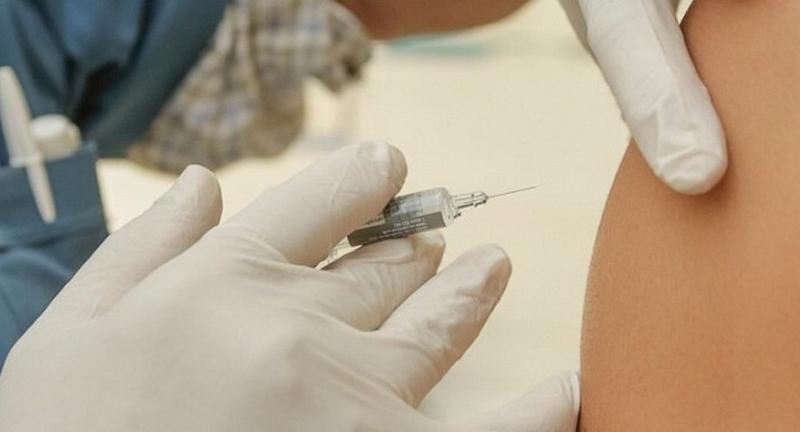
a) Vaccinations and
Immunizations (Maintaining Vitality)
Vaccinations and vaccinations are
critical for controlling the spread of infectious illnesses and safeguarding
individual and public health. They aid in the development of immunity to
numerous diseases, decreasing the intensity of illness and the danger of
consequences. Vaccination programs have been critical in eliminating or
managing several infectious illnesses across the world.
ii) Common Vaccines for Adults
Adults commonly receive
immunizations for influenza, tetanus, diphtheria, pertussis (Tdap), shingles,
and pneumococcal disease. Furthermore, vaccinations such as the COVID-19
vaccine have proven increasingly important in combating global health risks in
recent years.
b) Health Screenings (Maintaining
Vitality)
Health screenings are critical
for the early diagnosis and prevention of a wide range of medical disorders.
Blood pressure checks, cholesterol testing, mammograms (for breast cancer
screening), Pap smears (for cervical cancer screening), colonoscopies (for
colorectal cancer screening), and bone density scans (for osteoporosis
screening) are all common forms of health screenings for adults.
ii) When to Schedule Screenings
The scheduling of health tests is
determined by personal risk factors, age, and gender. Regular check-ups with a
healthcare practitioner might assist in determining the best screening regimen.
Adults should, in general, undergo a baseline health evaluation in their early
adulthood and then follow suggested screening recommendations.
c) Healthy Habits (Maintaining
Vitality)
One of the most significant
measures people may take to enhance their health is to quit smoking. Tobacco
use is a significant risk factor for lung cancer, heart disease, and
respiratory diseases. Smoking cessation programs, support groups, and
pharmaceuticals are available to help people quit smoking and live better
lives.
ii) Limiting Alcohol Consumption
Excessive alcohol use can result
in a variety of health complications, including liver damage, addiction, and
mental health problems. Individuals must drink in moderation and get treatment
if they are addicted to alcohol. Support groups, therapy, and recovery programs
are excellent options for anyone attempting to cut back on their alcohol
intake.
iii) Avoiding Harmful Substances
It is critical for general health
to avoid dangerous substances such as illegal drugs and prescription medication
abuse. These drugs can have serious physical and psychological repercussions.
Individuals battling with substance misuse must seek expert support and
recovery options.
7) Role of Environmental and
Lifestyle Factors in maintaining Vitality
a) Clean Air and Water
i) The Impact of Environmental Factors on Health
Air and water quality, for
example, have a significant influence on an individual's health. Poor air
quality can aggravate allergies, cause respiratory problems, and raise the risk
of cardiovascular disease. Waterborne infections and long-term health concerns
can be caused by contaminated water. Pollutants in the environment can also
lead to chronic illnesses such as asthma and cancer.
ii) Ways to Improve Air and Water Quality
Reducing exposure to indoor
pollutants such as cigarette smoke or allergies, as well as employing air
purifiers, can help to improve air quality. Efforts to minimize emissions from
automobiles and industries are critical in outdoor situations. Water quality
may be improved by good sanitation, sewage treatment, and industrial discharge
control. Individuals can also filter their tap water or purchase bottled water
from reputable sources.
b) Stress Reduction (Maintaining
Vitality)
i) Creating a Relaxing Environment
It is critical to create a
calming environment for stress reduction. This might involve creating a
tranquil and clutter-free living area, using relaxing colors, and adding
natural features such as plants. Reduced noise pollution and the implementation
of a daily routine that includes relaxation techniques such as deep breathing
exercises or meditation can help to create a less stressful atmosphere.
ii) Incorporating Stress-Reducing Activities
Stress-relieving activities are
critical for mental and emotional well-being. Hobbies, spending time in nature,
and practicing mindfulness can all help to reduce stress. Regular physical
exercise and appropriate sleep are also important in stress management.
Furthermore, creating limits and managing time properly can help to lessen
stress associated with work or personal obligations.
c) Work-Life Balance (Maintaining
Vitality)
i) Balancing Career and Personal Life
Work-life balance is critical for
general well-being. This entails striking a balance between one's work and
personal obligations. It's critical to understand that overcommitting to work
can lead to burnout, while ignoring one's job might result in financial
difficulty. Balancing these factors enables people to achieve in their jobs
while still having a meaningful personal life.
ii) Strategies for Achieving Work-Life Balance
Setting firm limits is an essential method for attaining work-life balance. This entails determining what you're prepared to give up and what you're not, as well as conveying these limits to everyone in your life who will be impacted by them. It's also crucial to prioritize a few things every day, which may help you better manage your time and energy.
Work limits are the guidelines we set for ourselves to provide a framework for working and spending time with our friends and family. They assist us in distinguishing between our job and personal lives.
Another important method for achieving work-life balance is self-care. This is taking time to recharge, recognizing your self-care requirements, and scheduling activities that help you relax and refresh. Mindfulness and meditation, regular physical exercise, and taking breaks are all examples of self-care activities.
Time management is a critical method for establishing work-life balance. This might include making a strategy for each day, keeping a closed list of duties, and minimizing distractions. It's also crucial to assign responsibilities when required to minimize fatigue and to avoid micromanaging too many things.
Work schedule flexibility may be provided via technology, allowing for a better work-life balance. This is especially useful for individuals who work from home since it allows them to distinguish between work and leisure time.
Finally, soliciting assistance from employers and coworkers when necessary can help to distribute burden and reduce work-related stress. This might include requesting assistance with work, talking openly and assertively about your requirements, and assembling a supportive team around you.
8) Monitoring and Tracking
Your Vitality
a) Keeping Health Records
(Tracking Vitality)
i) Importance of Health Records
Keeping detailed health records
is essential for efficiently tracking and maintaining one's health. Health
records contain a detailed history of medical illnesses, treatments, and
vaccines. They are critical for accurate diagnosis, treatment planning, and
providing healthcare practitioners with an accurate picture of an individual's
health history.
ii) Tools for Recording Health Data
There are several technologies
available for collecting health data. Healthcare practitioners frequently
utilize electronic health records (EHRs) to document patient information.
Individuals can also keep personal health notebooks or use health apps to keep
track of symptoms, medicines, and lifestyle variables. Wearables and smart
health technologies may also automatically gather and transfer health data for
convenient monitoring.
b) Regular Check-Ups (Tracking
Vitality)
i) The Role of Healthcare Professionals
Regular medical check-ups are
essential for preventative treatment and early diagnosis of health problems.
Physical examinations are performed by healthcare practitioners, who also
evaluate health data and request required screenings or tests. They provide
professional advice on how to live a healthy lifestyle and manage chronic
diseases.
ii) Scheduling Routine Health Check-Ups
The frequency of routine health
examinations varies according to age, gender, and individual health condition.
Adults should see their primary care physician at least once a year. Mammograms
and colonoscopies, for example, should be scheduled as suggested by healthcare
experts depending on risk factors and age.
c) Health Apps and Wearables (Tracking
Vitality)
i) Overview of Health Monitoring Apps and Devices
Individuals can check their
vitality with the use of health monitoring applications and wearables. These
applications may track a variety of health metrics, such as physical activity,
heart rate, sleep habits, and diet. Wearable gadgets capture real-time data and
frequently sync with smartphone apps for convenient access and analysis, such
as fitness trackers and smartwatches.
ii) How to Use Them Effectively
Individuals should choose health
monitoring applications and wearables that correspond with their health
objectives and interests in order to get the most out of them. Inputting data
and analyzing insights from these technologies on a regular basis can assist
individuals in making educated decisions regarding their well-being. It's also
critical to check the quality and security of these devices and applications, as
well as to consult with healthcare specialists before interpreting health data
or making major lifestyle changes based on the data obtained.
9) Conclusion
Understanding vitality barometers
is like having a compass to excellent health and well-being. This blog has
covered mental and emotional health, physical fitness, environmental and
lifestyle variables, and more. All of these factors are important for a healthy
and fulfilled existence.
We've discussed stress
management, positive relationships, and emotional resiliency. We've also talked
about the benefits of regular exercise, flexibility and strength training, and
preventative health. We've also stressed the significance of clean air and
water, stress reduction, and work-life balance and how these might affect our
health.
We've also stressed the need of
health records, frequent checkups with doctors, and new health applications and
wearables.
As we complete this crucial
indicator series, remember that good health is a lifetime pursuit. It involves
devotion, self-awareness, and educated decision-making. By paying attention to
these vitality indicators, we empower ourselves to take responsibility of our
health, happiness, and contentment. Let's go on this trip together, and may our
comprehension of these key signs lead to a better, more vibrant existence.
FAQ’s
Answer: Vitality refers to
a state of being full of life, energy, and vigor.
2.
Why is vitality important for overall well-being?
Answer: Vitality is
essential because it impacts our physical, mental, and emotional health,
contributing to a balanced and fulfilling life.
3. What are the
key indicators of vitality?
Answer: Key indicators of
vitality include mental and emotional well-being, physical fitness, and
environmental and lifestyle factors.
4. How
can I improve my mental and emotional well-being?
Answer: Strategies include
stress management, building emotional resilience, and nurturing positive
relationships.
5.
What is stress management, and why is it important?
Answer: Stress management
involves techniques to reduce and cope with stress, which is crucial for
preventing its negative impact on health.
6. How
can I build emotional resilience?
Answer: Building emotional
resilience involves developing the ability to adapt and bounce back from
adversity through practices like mindfulness and self-care.
7.
What is the connection between relationships and well-being?
Answer: Positive
relationships provide emotional support and contribute to overall well-being by
reducing stress and promoting happiness.
8.
What are some tips for cultivating positive relationships?
Answer: Tips include
effective communication, active listening, spending quality time, and conflict
resolution skills.
9.
What are the benefits of regular exercise for vitality?
Answer: Regular exercise
improves cardiovascular health, reduces stress, enhances mental well-being, and
helps maintain a healthy weight.
10.
How much exercise should I aim for weekly?
Answer: Adults should aim
for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes
of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week.
11.
Why is flexibility and mobility important for vitality?
Answer: Flexibility and
mobility improve joint health, reduce injury risk, and enhance overall
functional capacity.
12.
What are some simple exercises to improve flexibility?
Answer: Exercises like
yoga and stretching routines can help improve flexibility.
13.
How does strength training contribute to vitality?
Answer: Strength training
helps build and maintain muscle mass, improve metabolism, and enhance overall
physical health.
14.
What are some simple strength-building exercises I can do?
Answer: Bodyweight
exercises like push-ups, squats, and planks are effective for building
strength.
15. Why are
vaccinations important for preventive health measures?
Answer: Vaccinations are
crucial for preventing the spread of contagious diseases and protecting public
and individual health.
16. What are common vaccines
recommended for adults?
Answer: Common vaccines
include those for influenza, tetanus, shingles, and pneumococcal disease.
17. What types of health
screenings should I consider?
Answer: Health screenings
may include blood pressure checks, cholesterol tests, mammograms, Pap smears,
and colonoscopies.
18.
How often should I schedule health screenings?
Answer: The frequency of
screenings varies based on age and individual risk factors. Consult your
healthcare provider for guidance.
19. How can I quit
smoking for better health?
Answer: Smoking cessation
programs, support groups, and medications can help individuals quit smoking.
20.
How can I limit alcohol consumption for my well-being?
Answer: Setting limits, seeking support, and considering counseling can help limit alcohol consumption.
-min.jpg)









Comments
Post a Comment